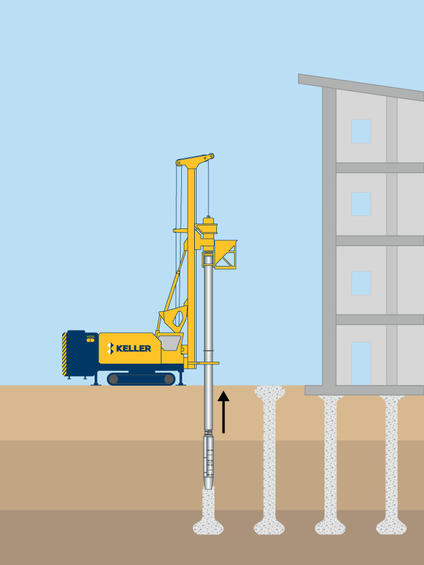
Vibro concrete columns involve constructing concrete columns with a bottom-feed, down-hole vibratory probe to transfer loads through weak strata to a firm underlying stratum.
Common uses
Process
A bottom-feed, down-hole vibratory probe is advanced through the weak strata to the underlying firm stratum. The vibrator densifies granular-bearing soils. Concrete is then pumped through the bottom-feed tremie tube. The vibrator is raised and lowered within the bearing depth several times to construct an expanded base. The vibrator is then raised to the surface as concrete fills the void created by the vibrator during extraction. Typically, the vibrator also re-penetrates the top of the column to construct an enlarged head, which a geogrid-reinforced soil-relieving platform can overlie.
Advantages
Quality assurance
Vibro rigs can be fully instrumented with an onboard data acquisition system. Data from the system, such as amperage and lift rate, can then be recorded and displayed in real time alongside specified target values on an in-cab monitor. This monitoring allows the operator to correct any deviations in real-time during the construction process to keep the vibro compaction within project specifications.real time